Non Cancer
Vascular and Non Vascular Interventional Surgeries can be performed through pin hole without causing significant morbidity and hospital stay.
Non Cancer Interventions:
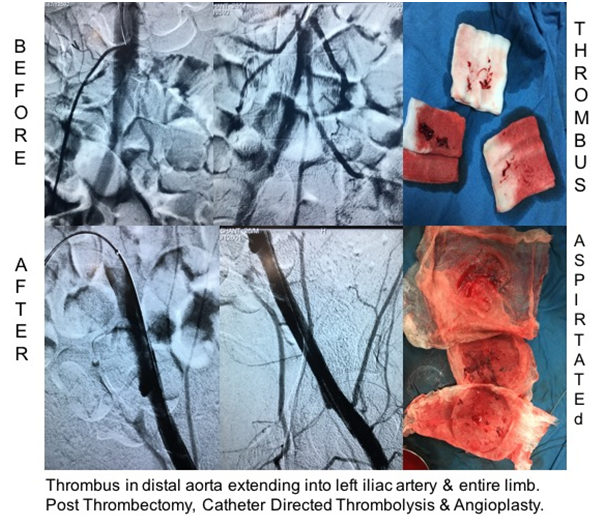
Thrombectomy/ Thrombolysis
Formation of clots in blood vessels i.e. arteries or veins is called as thrombus. This causes obstruction of blood flow which further leads to tissue/ organ ischemia and gangrene. This can be catastrophic if thrombus enters lungs (pulmonary embolism) and can also cause heart attack or stroke. In Cath Lab suite by passing catheters and wires into arteries and veins thrombus can be removed or it can be dissolved by injecting thrombolytic medicine directly into the clot.
To prevent migration of clot from legs into lungs, heart, brain etc. Inferior Vena Cava Filter (IVC Filter) is put. This holds major chunk of thrombus within it while patient can take oral medications to dissolve clot.
Case: Young boy with pain in left leg. USG Colour Doppler showed acute on chronic thrombus extending from distal aorta to popliteal artery.Mechanical suction thrombectomy and 48 hours thrombolysis done.
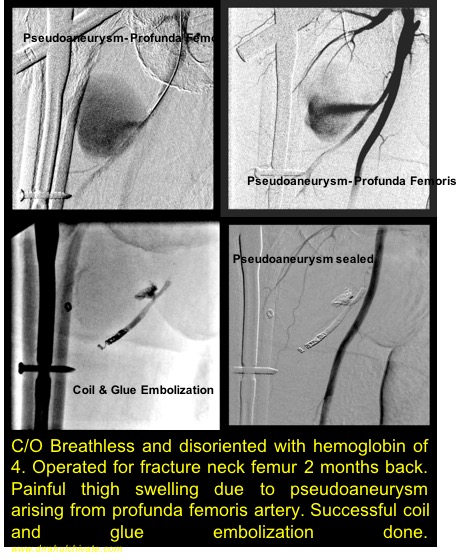
Bleeder Management
Bronchial Artery Embolization- Hemoptysis- Lung cavities in tuberculosis
Gastro Intestinal Bleeding- Bowel ulcers, diverticulitis.
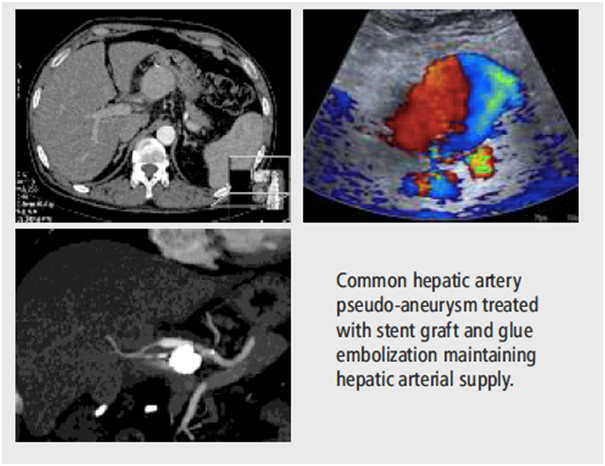
Post operative bleeding- Slipped suture, Pseudoaneurysm
Uterine Artery Embolization- Post delivery, For reducing size of fibroids
Genito- Urinary bleeders- Hematuria
Head and Neck bleeders- Post operative slipped suture or pseudoaneurysm, Large vascular tumours
Re surgery in post operative bleeders can be very morbid. Patient many times cannot tolerate this. Internal bleeding can be stopped with the help of catheters without any major surgery. In this active extravasation of contrast is detected under X ray in Cath Lab suite: artery is blocked using embolizing material.
Advantage:
Non surgical
No cuts. No stitches.
Sclerotherapy
Indications:
Arterio- venous malformation
Veno Venous malformation
LymphoVenous malformation
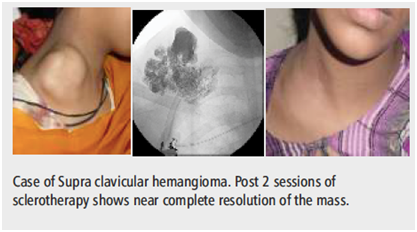
Tumour of vessels i.e. Arteries and Veins which are called as Arterio-Venous, Veno- Venous or Lympho-venous malformation can be treated by gold standard method of sclerotherapy in Cath Lab suite under Ultrasound guidance. This entity is commonly seen in pediatric age group and young adults. Pre sclerotherapy angiography is done to map the extent of disease and vessel feeders. Thin needle is punctured directly into this malformation and drug is injected. It has replaced surgery which would cause significant bleeding and recurrence.
Advantage
Day care procedure
Can be done under sedation
No cut. No stitches.
Significant regression in size in 1 session
Sessions can be repeated till regression
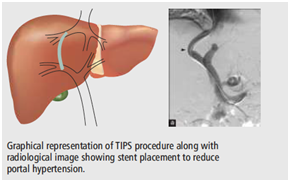
Trans Jugular Intrahepatic Porto- systemic Shunt (TIPS) and Balloon Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration (BRTO): Cirrhotic Liver.
Indication:
Cirrhotic liver- Portal hypertension
Variceal Bleeding
Refractory Ascites
Budd Chiari Syndrome
Hepatic hydrothorax
Hepato-Veno-Occlusive disease
Portal Vein thrombosis
Esophageal varices and Gastric Varices are caused by portal hypertension which makes them bleed into esophagus or stomach. Patients have hematemesis or malena. A channel (TIPS) is made connecting hepatic vein and portal vein to reduce portal hypertension. For left sided portal hypertension with gastric bleeding Gastro-renal shunt is blocked using sclerosant (BRTO). Surgeries to create shunt needs prolonged hospital stay and increases morbidity. Patient needs to take anti-coagulants to keeps the channel patent.
Advantage
No cutting. No stitches.
Less morbidity
Inferior Vena Cava Plasty and Stenting
Inferior Vena Cava is a major vein in the abdomen which drains veins of lower limbs and abdomen to heart. IVC obstruction can cause significant pain in abdomen and edema of limbs. A condition called as Budd Chiari Syndrome;there is obstruction of IVC or hepatic veins causing liver congestion and less functioning. This block can be crossed using wire and can be opened by dilating balloon (IVC plasty) or stenting in Cath Lab suite. Surgery can be avoided.
Advantage
Done under local anesthesia
Less morbidity
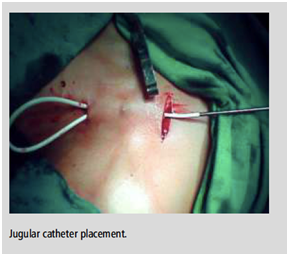
Jugular/Vascular Access
Vascular access especially through internal jugular vein is required for dialysis catheter, chemo port or tunneled catheter placement. Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC line) is done under local anesthesia with precise placement of the catheter tip at the junction of Superior Vena Cava (SVC) and right atrium.
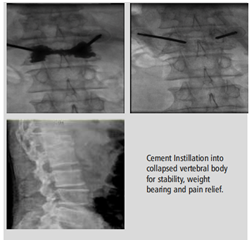
Vertebroplasty/ Kyphoplasty
Indications:
Collapse/ Compression of vertebra- Osteoporotic, Traumatic, tumour/ metastases
Kyphotic deformity correction.
Procedure is done under local anesthesia under fluoroscopy, Cath Lab suite by injecting cement through a needle in vertebral body. Cement gives stability to the vertebra and reduces pain and morbidity.
Advantage:
Day Care procedure
Immediate pain relief
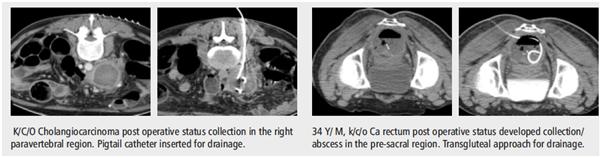
Pig Tail Drainage
Indication:
Fluid collection- Pleural fluid/ Ascitic fluid
Abscess drainage
Post operative seroma or abscess
Drainage catheters are placed precisely under CT scan or ultrasound guidance into the cavity to drain out fluid or pus.
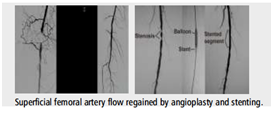
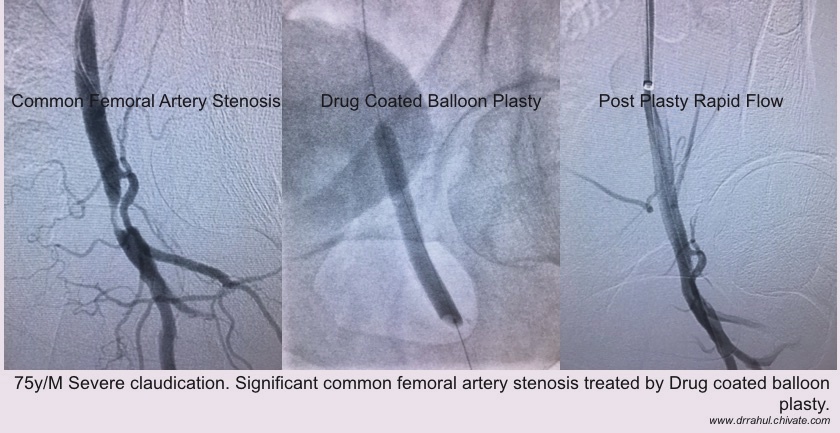
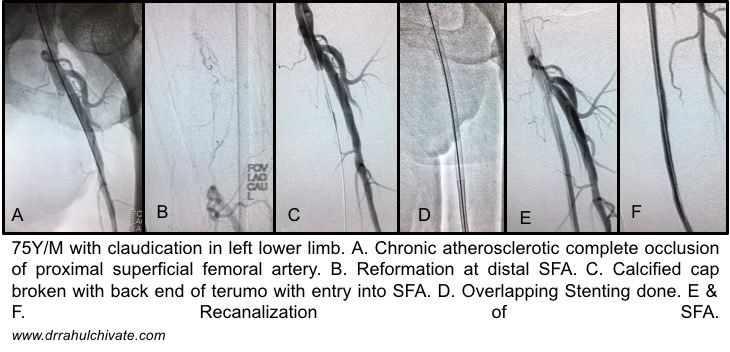
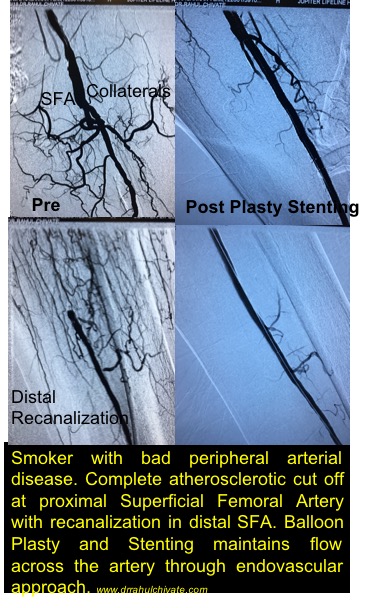
Diabetic Non Healing Ulcer: Peripheral Arterial Disease
Indication:
Atherosclerotic disease
Rest pain
Ulcer
Gangrene
Balloon Angioplasty or stenting is done for blocks in arteries of lower limbs improves blood supply to legs. Ulcer especially refractory to local dressing/therapy is acceleratedby improving the blood flow which improves oxygenation of tissues.
Advantage:
Day Care procedure
Promotes healing of long standing ulcers
No cutting. No stitches
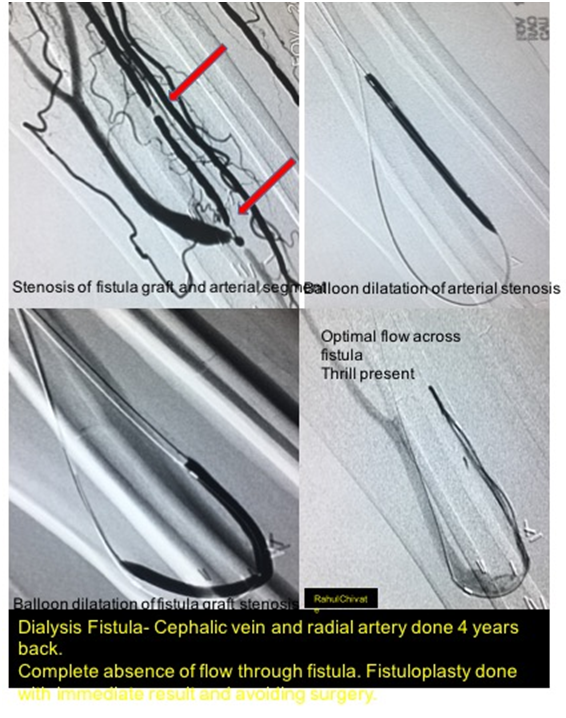
Dialysis Fistula Repair:
Chronic renal failure patient undergone Arterio-venous fistula for dialysis presented with complete absence of thrill. Fistula repair done by endovascular method. Surgery avoided.
Uterine Artery Embolization (UFE) for Fibroids
UFE is a non-invasive method for treating fibroids. This can be especially useful in women
having infertility, pain and bleeding due to fibroids. Surgical procedure like myomectomy or
hysterectomy is avoided. Hence, the recovery is very quick. Procedure is done under local
anesthesia and patient can be discharged the very next day and she can resume work within
5 days.
Pre-Embolization work up:
– Gynecology evaluation
– Ultrasonography
– MRI pelvis to rule out adenomyosis and malignancy
– Ovarian Function evaluation (Blood report- LH, FSH)
– Pregnancy test (- Blood report- beta HCG)
– No genital infection (Vaginal discharge if any)
– Blood tests- Complete blood count, Coagulation profile, Liver function and Renal
function tests, Viral Markers)
– Remove IUCD
Indications:
– Symptomatic Fibroids- pain, bleeding, infertility
– Generally small fibroids
– Infertility due to fibroids
Contra Indications:
– Infection
– Pregnancy
– Asymptomatic fibroids
– Doubt of malignancy or adenomyosis
– Blood thinner medications
– Renal problem
Complications/ Side effects:
– Post embolization syndrome- nausea, fever, dull ache
– Vaginal discharge
– Infection
– Amenorrhea
– Passage of fibroid material