Cancer
Interventional Oncology (IO) is one of the widely practiced field of medicine. IO can be helpful not only in diagnosis but treatment of inoperable large tumours. With help of Vascular and Non Vascular Interventions large tumors can be reduced in size, inoperable tumours can be operated and small tumours can be completely treated without surgery in day care settings.
Cancer Interventions:
Trans Arterial Treatment
Surgery, Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy are known modalities of treatment for cancer. TranArterial treatment or Trans Arterial Chemo Embolization is a concept by which the artery supplying the tumour is cannulated with catheters and the tumour is bombarded with anti cancer drug along with embolization material which blocks the blood supply of the tumour. This procedure is done in Cath Lab suite.It is very advantageous as smaller quantity of drug is required. Side effects of these drugs is minimal as
compared to routine systemic chemotherapy. Blockage of tumour feeder arteries also causes ischemia or cell death causing significant shrinkage of the cancer.
Trans Arterial Therapy:
Which tumor can be treated
Liver tumours- Hepatocellular carcinomas- Inoperable
Liver metastases – Metastases or spread to liver from cancers from other organs.
Head and Neck tumours – Downsizing of large inoperable cancer.
Orbital/Eye tumours – Retinoblastoma.

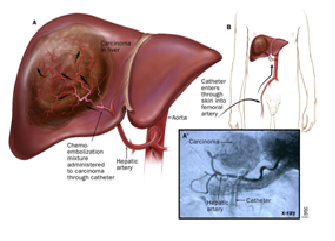
Liver Cancer treated with Trans Arterial ChemoEmbolization. A. Angiography image and B. CT scan images show deposition of drug in tumour.
Bland Embolization
This procedure is similar to transarterial chemo embolization without use of anti-cancer drug. In this procedure only embolizing material which blocks the arteries of the tumour is used causing shrinkage and necrosis of the cancer mass. It requires few sessions and patient can be pain free. Which tumours can be treated? Inoperable- Large Bone Cancers like- Giant Cell tumour, Chondroma, Hemangioma, Aneurysmal Bone Cyst. Advantage Maximum 1 day of hospital stay Done under local anesthesia No cut. No stitches. Can be repeated if tumour is large in size or new tumour is detected on follow up.
Bland Embolization of Bleeding Fibroid Uterus: A. Pelvic Angiography B. Selective Angiography C. Super Selective Angiography-Uterine Artery shows tumour blush in the uterus on left side. D. Post Bland embolization there is complete absence of
tumour blush and bleeding.
Case of Sacral Giant Cell Tumour: A. Antero-Posterior view and B. Lateral view show dense tumour blush from sacral (bone) tumour also involving right iliac bone. C. Post Embolization Angiography shows complete absence of tumour blush. Pain score reduced from 8 to 3.
Radio Frequency Ablation/ Thermal Ablation
Radio Frequency Ablation/ Microwave Ablation
It is a non- surgical, localized treatment that kills tumour with heat, while protecting healthy surrounding tissue. Interventional Radiologist inserts special needles (no incision, no stitches) called as electrodes and antenna into the the tumour under Ultrasound or CT scan guidance. The temperature is raised to more than 1000C to kill the tumour cells.
Advantage:
Day Care Procedure- Patient can resume daily activities next day.
Repeatability: Procedure can be repeated if there are multiple tumours or new lesion is detected on follow up.
Large tumours- Very large tumours can be treated in sessions. But it immediately reduces pain.
Which tumours can be treated?
Liver tumours- hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver metastases
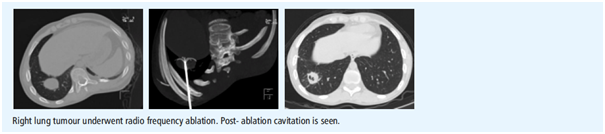
Lung tumours- inoperable primary tumour and metastases
Renal Tumours- Inoperable
Bone tumours- Osteoid Osteoma, Chondroblastoma, Ostoblastoma
Soft tissue tumours- Fibromatosis
Pre operative embolization
Pre Operative Embolization:
Case of Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma was to be operated. Being a vascular mass intra operative bleeding is can be very significant (more than 2-3 Lit) and would require blood transfusion. However, the tumour was embolized and intra operative blood loss was only 400cc.
Indication:
Hemangioma
Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
Glomustumours
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Hepatoblastoma
Angiosarcoma
Hemangioendothelioma
Angiomyolipoma
Metastases etc.
Some tumours are very vascular and when operated causes significant blood loss which requires blood transfusion and can be life threatening. This procedure is done in Cath Lab suite in which vascular supply of the tumour is blocked 24-48 hours prior to surgery.
Advantage:
Less or no blood loss. Less post operative stay and morbidity.
Clear operative field.
Necrosis of tumour causing less chances of recurrence.
Complete removal of tumour.
Portal Vein Embolization
Portal Vein Embolization;
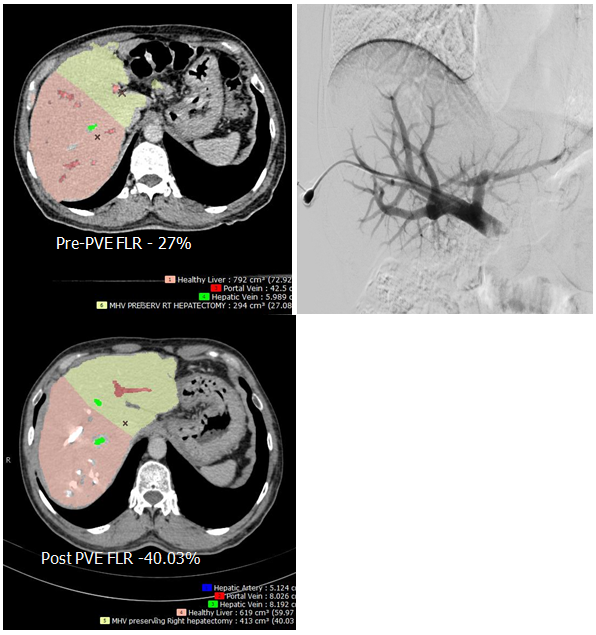
Case for Right Hepatectomy with liver metastases. Pre operative FLR- Future Liver Remnant was 27 %. Right Portal Vein Embolization done shows increase in FLR to 40% .
This procedure is done before liver surgeries. It helps to increase contra lateral liver volume which is essential for viability. More than 30% of residual liver volume (Future Liver Remnant) is recommended for functioning if patient is undergoing hepatectomy. This is done by percutaneous method and portal vein on same the side of tumour is blocked which causes compensatory hypertrophy of another lobe of liver. This procedure is done in Cath Lab suite.
Advantage
Day care procedure
Increases future liver remnant
Less morbidity and good operability
Biliary Interventions
Indication:
Obstructive Jaundice
Biliary leak
Percutaneous Biliary Drainage with stenting is done to drain bile or create a pathway for flowing bile into bowel. This reduces jaundice in cases of obstruction caused by stones and cancer of gall bladder, bile ducts, pancreas etc. In Cath Lab suite under local anesthesia and ultrasound guidance bile duct is punctured by needle and entire biliary tree is opacified with contrast agent. Type of block is identified which can be treated by stenting.
Advantage
Day care procedure
No cut. No stitches.
Serum Bilirubin level normalizes by 20-25 days.
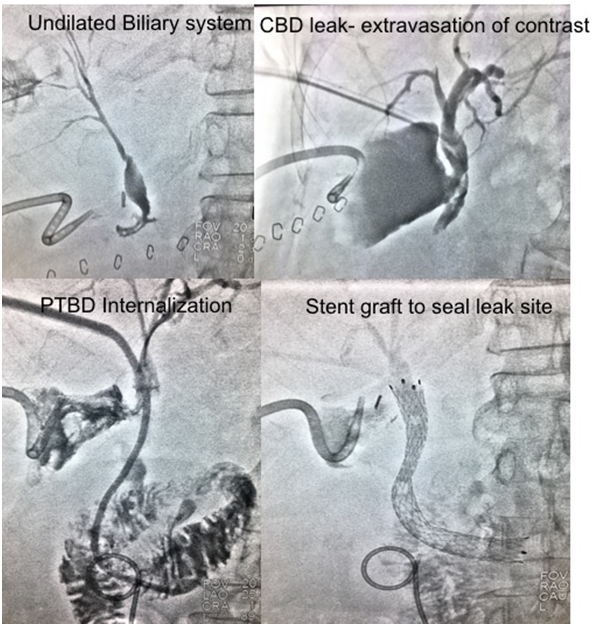
Post Gastrectomy with multiple nodal disease had common bile duct injury. Active biliary leak present for which drainage catheter was inserted. Biliary diversion done for undilated system and further stented to seal the leak site.
CT/USG guided Biopsy/FNAC
Treatment of any tumour or disease depends on tissue histopathology. This means small pieces of tumour needs to be removed to see under microscope. Using Ultrasound and CT scan guidance thin needles are placed precisely within the tumour and biopsy is done. Bone/ Vertebral biopsy is done using sharp needles which can penetrate bone.
Advantage:
Procedure is done under local anaesthesia.
Patient can resume activities immediately after procedure.
No cut. No stitches. No dressing required.